Scale Used to Describe the Extent of a Hazard Event
Extent can also incorporate characteristics such as. For example the Oxford dictionary defines common terms used to describe disasters as follows Oxford 2010.
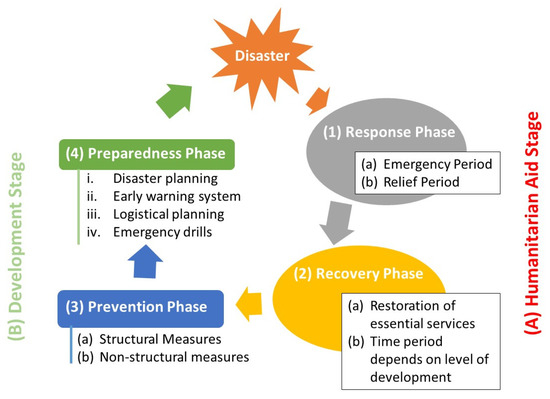
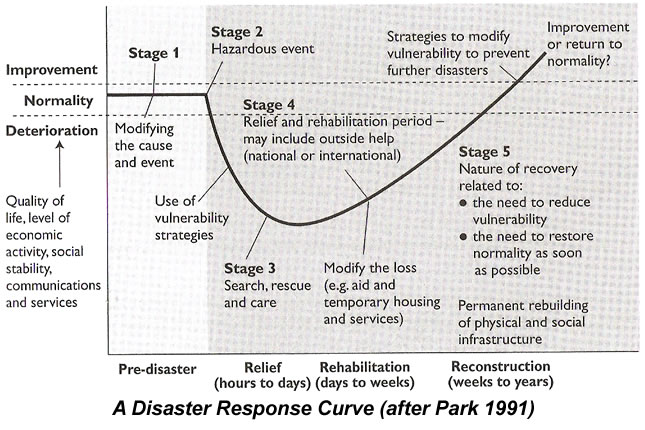
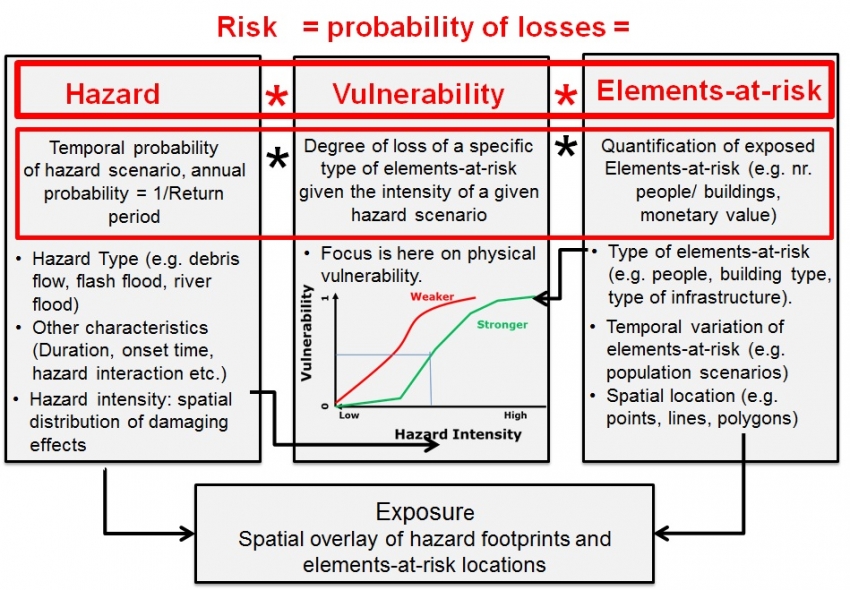
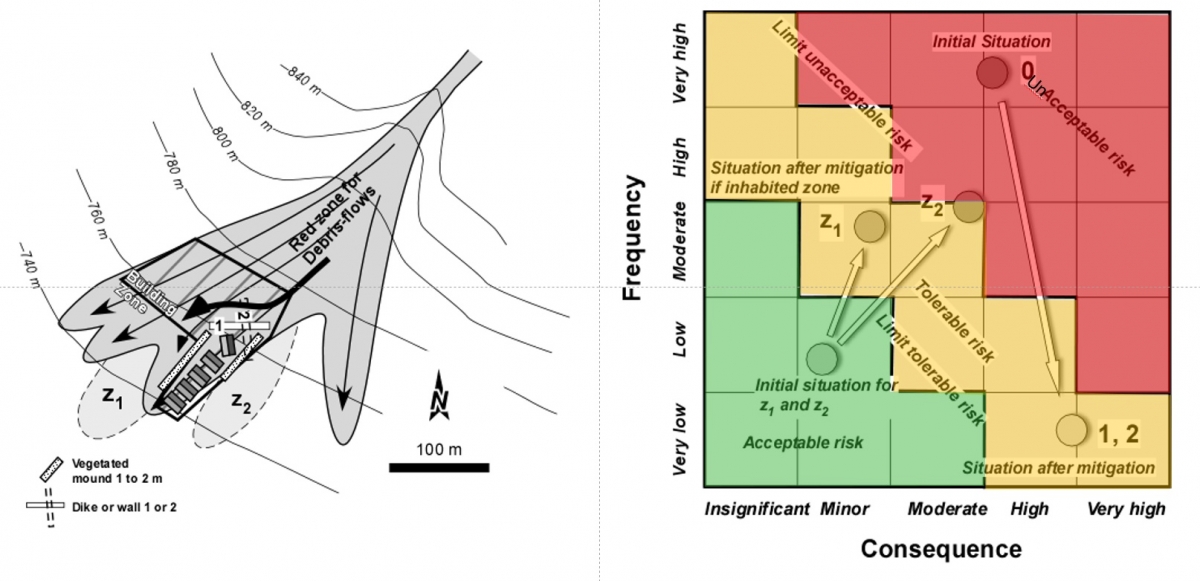
Chapter 2 Natural Hazard Risk Reduction In Project Formulation And Evaluation
An earth rigidity factor.

. Which of the following BEST describes what you should include in the updated risk assessment. Generally will describe the scale and extent of damage and disruption that may result from the scenario tsunami. Up to 10 cash back The magnitude of a natural hazard event varies in its frequency of occurrence over time in an inverse power relationship.
Only use one method to muteunmute yourself to avoid double muting. An event causing great and often sudden damage or distress. The moment magnitude scale MMS is used to describe the size of an earthquake.
543-1 presents the Richter scale magnitudes and corresponding earthquake effects. Spatial extent and duration of natural hazards in Germany. The hazard ratio describes the relative risk of the complication based on comparison of event rates.
Ash fall can travel million km2 and change global temperature tsunamis may spread effects 1000s of km. A hazard event is not likely to occur or is unlikely to occur with less than a 1 annual chance probability. Scientists talk about the occurrence of hazards of different intensities in terms of probabilties or return periods also known as recurrence intervals within the context of.
Distinguish between a hazard event and a a disaster. Describe the methods used to quantify the spatial extent and intensity of. It is calculated from.
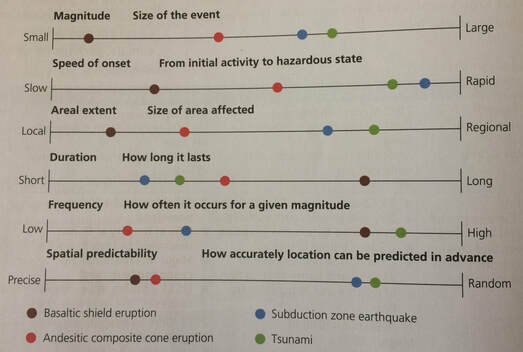
Hazards are the origins of disasters. AO2 Areal extent is an important factor because some impacts can be global eg. A hazard event may occur multiple times per year.
If you have a question or comment please use the chat box or the Raise Hand function on the top of your screen. Areal extent is one element of the hazard profile others include magnitude frequencydurationspeed of onset. Whereas impacts of rock and ash create huge.
Estimates of potential damage and economic loss to buildings can then be calculated. This alerts the facilitator that you would like to speak. Methods used to quantify the spatial extent and intensity of disasters include the Volcanic Explositivity Index VEI the Moment Magnitude Scale MMS looks at the energy released has succeeded the Richter Scale in many countries although the Richter Scale shaking amplitude of waves measured by a seismograph is still widely referred to in the media and the Saffir.
2 Frequent 100 annual probability. An event involving destruction or damage on a catastrophic scale. Click again to lower your hand after speaking.
_____ is an example of a scale you can use to describe the extent of a hazard event. Can create the wind hazard data from a historical or real-time event probabilistic event or from a user-defined scenario. Hazard ratios have also been used to describe the outcome of therapeutic trials where the question is to what extent treatment can shorten the.
The relationship is often depicted as log-normal Figure 1 where the magnitude increases linearly eg 1 2 3 whereas the frequency decreases as an inverse power function eg 13 19 181 with increasing. _____ is an example of a scale you can use to describe the extent of a hazard event. The amount of slip on the fault.
DMA 2000 Hazard Mitigation Plan Dutchess County New York 543-2 December 2015. 1 Occasional Between 10 and 100 annual probability of a hazard event occurring. A large-scale and violent event in the natural world.
Distinguish between a hazard event and a a disaster. Use video if possible to promote face to face. The moment magnitude scale abbreviated as MMS.
To provide data to the federal government about natural hazards threatening the nation D. Hazard Profiles Measuring Earthquakes. Explain why this distinction is not always completely objective.
It is helpful to use an established scientiic scale like the Modiied Mercalli Scale for earthquakes the Safir-Simpson scale for hurricanes or the Enhanced Fujita Scale for tornadoes. Richardson topographical damage scale C. Hazards occur at different intensities or magnitudes over different time scales sometimes known as temporal scales.
0 40 Rare Between 1 and 10 annual probability of a hazard event occurring. Fill in the blank. Explain why this distinction is not always completely objective.
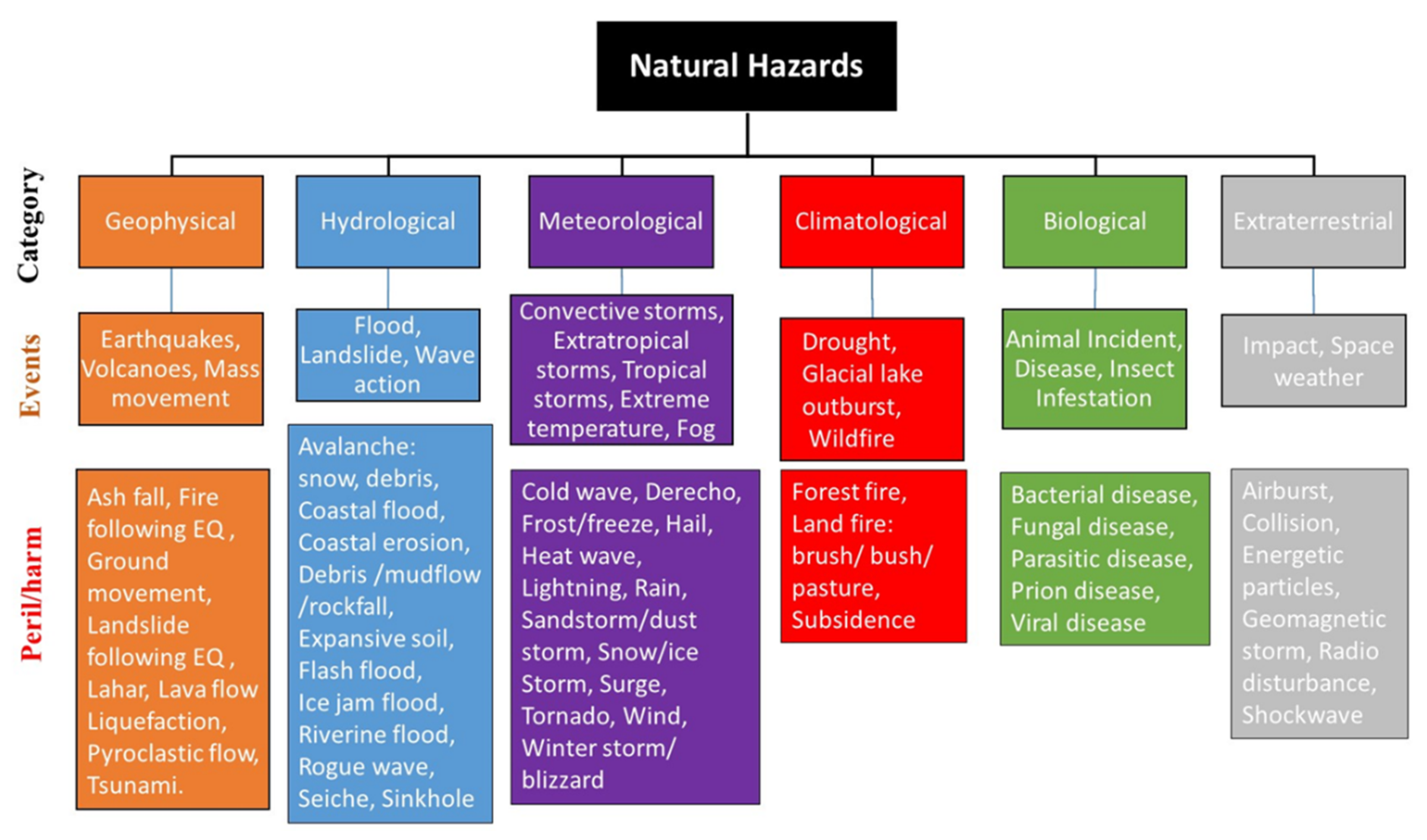
Denoted as MW or M is used by seismologists to measure the size of earthquakes in terms of the energy released. Describe the methods used to quantify the spatial extent and intensity of. According to the United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction UNISDR a hazard is a natural process or phenomenon that may pose negative impacts on the economy society and ecology including both natural factors and human factors that are associated with the natural ones.
To utilize the various hazard mitigation plan review procedures such as the direct read C. To provide a census on participation. The scales illustrate the sum of all single events contributing to the damage of the entire hazard event for example all lightning.
It is based on the seismic moment and is applicable to all sizes of earthquakes USGS 2012.

Five Point Likert Scale For The Impact Level Of Ppp Risk Download Table
1 5b Hazard Profiles A Level Geography Revision Edexcel
The Impact Of Hazards On People And The Environment Igeogers
Encyclopedia Free Full Text Natural Disasters Origins Impacts Management Html
Hazards And Disasters Risk Assessment And Response The Geographer Online

Hazards And Disasters Risk Assessment And Response The Geographer Online

Hazards And Disasters Risk Assessment And Response The Geographer Online

A Multi Hazard Framework For Spatial Temporal Impact Analysis Sciencedirect
Encyclopedia Free Full Text Natural Disasters Origins Impacts Management Html

Hazard Profiles A Level Geography Edexcel Revision Study Rocket

Hazards And Disasters Risk Assessment And Response The Geographer Online
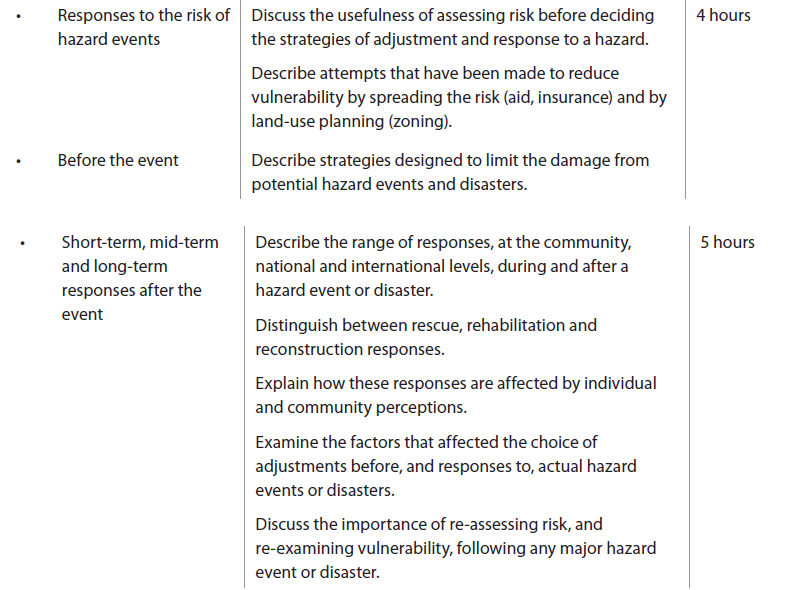
Hazards And Disasters Risk Assessment And Response The Geographer Online

Hazards And Disasters Risk Assessment And Response The Geographer Online
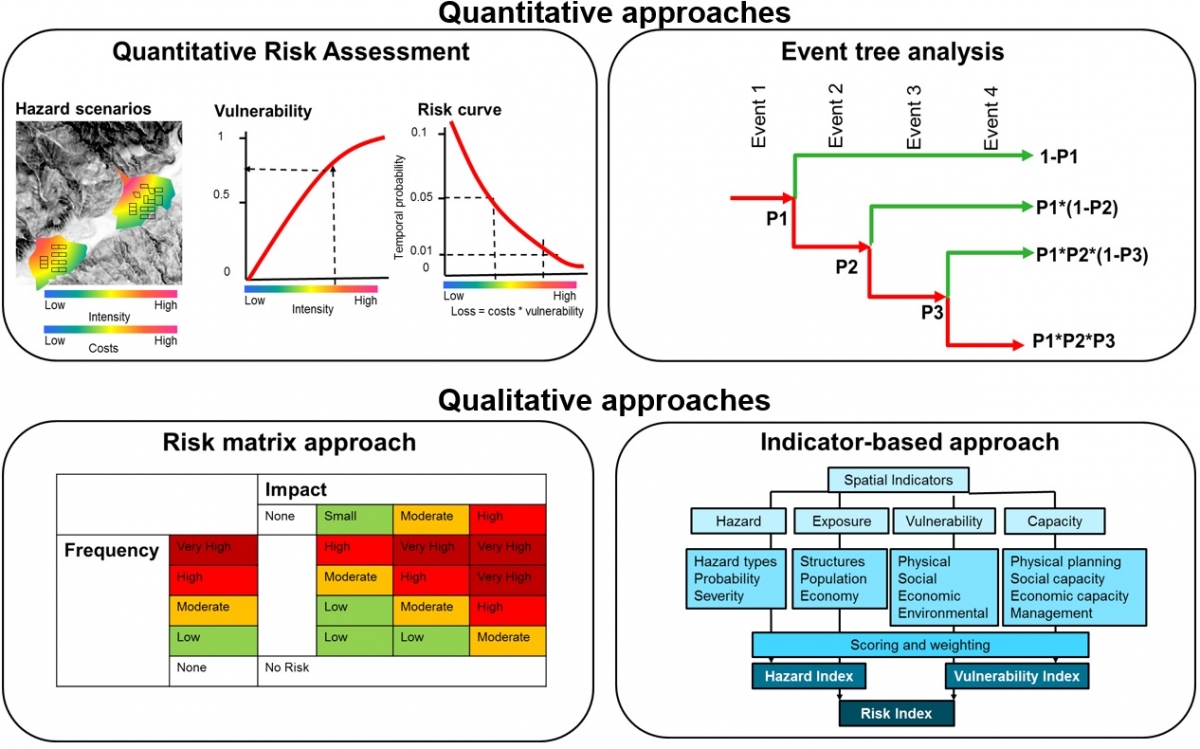
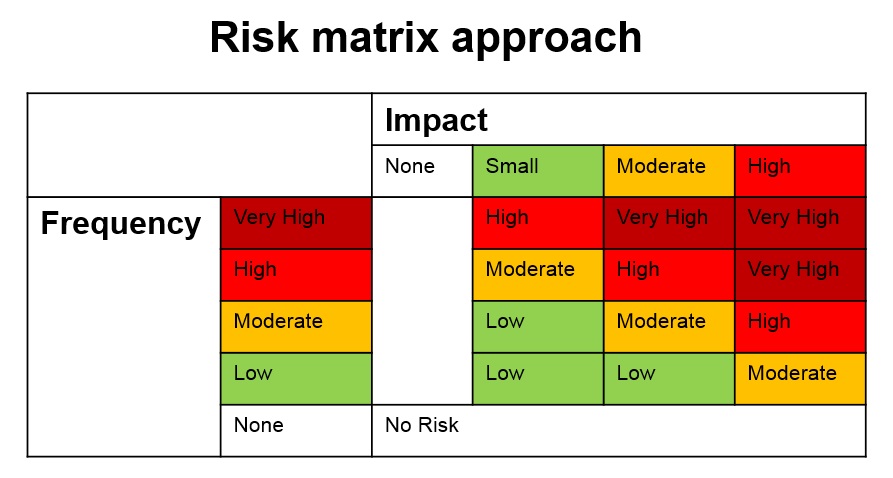
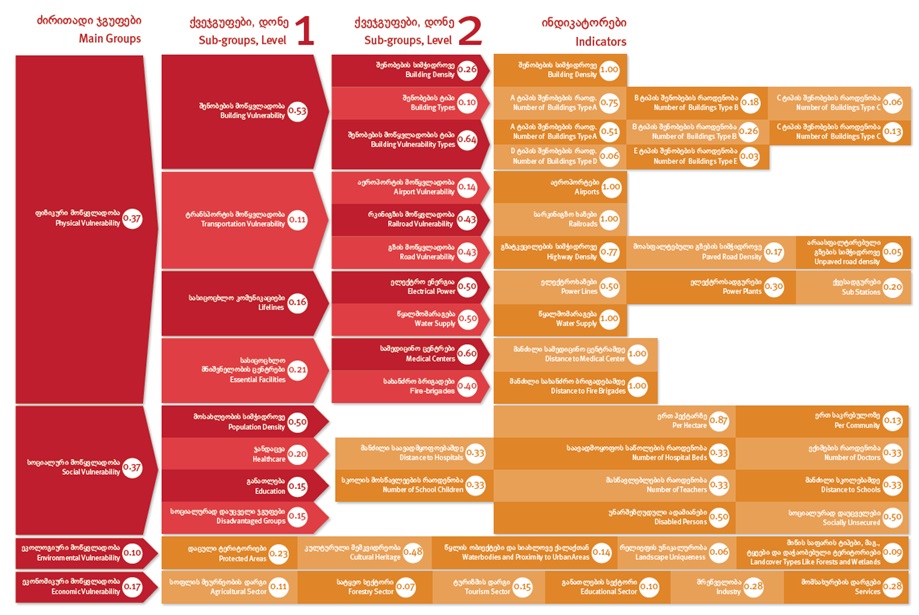

Comments
Post a Comment